|
What materials can we use for CNC machining
|
1. CNC Metal Materials |
CNC aluminum and aluminum alloy processing | Characteristics of aluminum and aluminum alloys: light weight, high strength, good thermal conductivity, good processing performance, and low cost.
Applications: aerospace parts, automotive components, electronic radiators, etc.
Common models: 6061 (corrosion-resistant), 7075 (high hardness), aluminum alloy 5083, aluminum alloy 6060, aluminum alloy 6082, and customized aluminum alloys are also available. |
CNC steel and carbon steel processing | Features: High hardness, excellent wear resistance, suitable for high-strength demand scenarios.
Applications: mechanical parts, molds, shafts, etc.
Subdivision types: 45 steel (balanced comprehensive performance), 40Cr (excellent hardenability) S50C、Q235、 Mold steel 718 NAK 80、 Steel 1.7225 SKD11、SKD61、S136, Customized steel alloys are also available. |
CNC stainless steel processing | Features: Corrosion resistance, good ductility, weldability, and strong polishing ability.
Application: Medical devices, food processing equipment, chemical composition 13.
Common models: 304, 316Cr12, SUS 303, SUS 304 (universal type) SUS 316L、17-4PH、 2205, there are also customized stainless steel alloys that are more corrosion-resistant. |
CNC copper and copper alloy processing | Features: Excellent conductivity/thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance.
Applications: electrical connectors, heat sinks, decorative parts.
Common types: brass (valves, water pipes), copper (conductive components) H62、H69、H56、H96、 Beryllium copper C17200(QBe2)、C17510(CuNiBe)、C17500(CuCoBe)、C17300(CuBe1.7)、C17300(CuBe1.7)、C18000(CuNiCrSi)、C18150(CuCrZr)、C18000(CuNiCrSi)、 There are also customized copper and brass alloys available. |
Titanium alloy CNC machining | Features: High strength, high temperature resistance, good biocompatibility, but difficult to process.
Applications: Medical implants, aviation engine components, high-end sports equipment.
Common types: TC4, TC5, TA2, TA5 |
2. CNC engineering plastic processing |
CNC machining of ABS | Features: impact resistance, easy processing, low cost.
Applications: Electronic product casings, toys, daily necessities. |
CNC machining of polyoxymethylene (POM) | Features: High rigidity, low friction coefficient, and wear resistance.
Applications: gears, bearings, precision mechanical parts. |
PC (polycarbonate) CNC machining | Characteristics: Transparent, heat-resistant, and impact resistant.
Application: Safety lenses, lampshades, electronic device casings. |
Numerical Control Machining of Nylon (PA) | Features: Wear resistant, self-lubricating, and resistant to chemical corrosion.
Applications: gears, pipelines, automotive parts . |
CNC machining of PEEK (polyetheretherketone) | Features: High temperature resistance (260 ℃), chemical corrosion resistance, high strength.
Applications: Aerospace components, medical equipment, semiconductor equipment.
We also offer customized polymer processing services for PMMA acrylic/acrylic, POM/formaldehyde/formaldehyde, PA/nylon/polyamide, PP polypropylene, PTFE/polytetrafluoroethylene, PVDF/polyvinylidene fluoride, UHMW PE/ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene |
3. CNC composite material processing |
Carbon fiber CNC machining | Features: Light weight, high strength, and fatigue resistance.
Applications: drone framework, racing parts, high-end sports equipment. |
CNC machining of glass fiber | Features: Low cost, good insulation, corrosion resistance.
Application: Ship components, building structural components. |
4. CNC machining of other materials |
Wood processing CNC | Features: environmentally friendly, easy to process, and aesthetically pleasing texture.
Applications: furniture, decorative carving, building components.
|
CNC machining of stone (marble, granite) |
Features: High temperature resistance, high hardness, and strong decorative properties.
Applications: Architectural reliefs, countertop carvings, artworks. |
CNC glass processing | Characteristics: High precision drilling requires specialized cutting tools.
Application: Decorative lighting fixtures, building glass curtain walls.
|
Precautions for material selection in CNC machining |
Difficulty in CNC machining: Materials such as titanium alloy and PEEK require special tools and processes.
Cost control: Carbon steel and aluminum alloy are suitable for large-scale economic production.
Environmental adaptability: Corrosion resistant materials such as stainless steel or PEEK are preferred in the medical and food fields.
By selecting materials reasonably, CNC machining can meet the high-precision manufacturing needs of various fields such as industry, healthcare, and consumption |
|
|
Surface treatment options supported by CNC machining
Anodic oxidation |
Type II anodizing improves corrosion resistance and can be used as a basis for surface treatment of paints and other finishes. Note: The anodizing effect may vary among different materials.
Note:
Using dyes to affect the surface color of parts
Type II coating is prone to wear and may bleach or fade under prolonged direct sunlight
Can customize color (RAL) |
Dusting |
Use uniformly applied thermosetting coating to provide a continuous protective color surface for the parts. Compared to traditional spray painting, powder coating surface treatment is usually tougher or even more uniform. Metals such as aluminum and steel can be effectively coated with polymer powder.
Note:
There are many options for powder coating, and customers need to choose different types of powder coating based on the functionality of the product |
Electropolishing |
Electrolytic polishing refers to an electrochemical process that can clean steel components, reduce corrosion, and improve appearance by making the metal brighter. However, electrolytic polishing may have a certain impact on product size (reduction) while improving the surface smoothness of the product.
Note:
Reduce corrosion
Brighter appearance |
Passivation |
This is a colorless coating that improves the corrosion resistance of 200 series, 300 series, and age hardened corrosion-resistant stainless steel by removing surface burrs.
Size changes: Passivation treatment may cause small changes in metal size
Surface roughness: Passivation treatment may result in a slight increase in surface roughness.
Not applicable to all metals: Passivation treatment is typically used for metals such as steel and stainless steel, and may not be suitable for some other types of metals. |
Electroless nickel plating |
Chemical nickel plating refers to the application of a uniform nickel coating on the surface, which can prevent corrosion, oxidation, and wear of irregular surfaces.
The wear resistance of nickel plated coatings may be relatively low, especially under high friction or wear conditions, where the coating may be damaged.
Nickel plating coating may affect the weldability of the product, making the welding process more difficult.
Note:
Prevent corrosion, oxidation, and wear of irregular surfaces
Brighter appearance |
gold-plating |
Gold plating has good corrosion resistance and rust resistance. Gold plating has low contact resistance, excellent conductivity, and solderability.
Note:
Golden like appearance
Improve corrosion resistance and rust prevention ability |
Electroplated/hot-dip galvanized |
Electrogalvanizing/hot-dip galvanizing refers to the electroplating of a thin layer of zinc metal onto the surface of another metal object (called a substrate). The zinc coating forms a physical barrier to prevent rust from reaching the underlying metal surface.
1: Galvanized coatings may reduce the electrical conductivity of metals, which may be a disadvantageous factor for certain electrical applications.
2: Once the galvanized coating is damaged, repair or maintenance may be relatively difficult.
3: The presence of galvanized coating may increase the hardness of the metal surface, thereby reducing the plasticity of the metal.
4: Galvanized surfaces may affect the welding performance of products, as the presence of zinc may result in the production of undesirable gases during welding, affecting welding quality.
5: Galvanized coatings may become brittle under certain conditions, especially at high temperatures, which can lead to cracking or detachment of the coating.
Note:
Improve corrosion resistance |
Blackening (black oxidation) |
Black oxide is a coating formed by the transformation of ferrous materials (such as steel and stainless steel), which can cause the surface of the material to turn black. It can be used to reduce reflection and glare, and has a certain degree of corrosion resistance without affecting part size. |
Annealing |
Annealing is a metal heat treatment process. The annealing process refers to heating a metal to or near the temperature at which recrystallization begins without changing the stress. After heating, the metal is usually cooled to room temperature in an oven or in sand.
Effect:
Improving the cold working ability of metals helps to reduce their hardness and improve their mechanical properties, making them easier to process and form the desired shape. |
Surface hardening (nitriding) |
Surface hardening is a heat treatment process that hardens the surface metal while maintaining the softness of the underlying metal. As the name suggests, carburizing is the process of introducing carbon or nitrogen into low-carbon alloys at high temperatures to increase surface hardness. It should be noted that nitriding treatment may increase surface roughness, improve the hardness and wear resistance of the metal surface. |
Tempering |
Tempering is a heat treatment method that involves heating a metal to a temperature below the critical point and then reducing its hardness. The temperature is adjusted according to the required reduction in hardness and varies depending on the type of metal.
Note:
Reduce hardness
Increase elasticity and plasticity
Reduce yield strength and tensile strength |
Quenching |
Quenching is different from surface hardening in that it not only hardens the surface, but also gives the entire alloy a relatively similar hardness. This can be achieved by introducing carbon into the alloy matrix and repeatedly quenching it in salt water or water, or by oil quenching. It should be noted that the quenching strength needs to be determined based on the characteristics of the material. If the quenching requirement is too high, it may cause the product to crack.
Note:
Hardened surface layer, wear-resistant, wear-resistant, and deformation resistant
The internal core of the material maintains toughness and ductility |
Hard anodizing (type III) |
The hard anodized (Type III) layer can produce a thicker standard anodized layer, making it more durable and wear-resistant. Can be used as a base for paint or other finishes.
Note:
Due to thickness, the color may appear slightly darker
Can request custom color (RAL) |
Customized |
If you choose custom surface treatment in the IQE real-time quotation engine, it will require manual review by the Xomtry Power Technology engineering team, which usually takes 1-2 working days.
Note:
The manual review of custom surface treatment requirements by the engineering team does not guarantee a 100% quotation. |
What CNC machining machinery do we have
CNC machining involves various types of mechanical equipment, with the following core machinery types and their functions:
|
CNC lathe | Horizontal lathe: The spindle is arranged horizontally, suitable for machining shaft and disc parts, with high stability and easy automation control.
Vertical lathe: The spindle is arranged vertically, suitable for processing large circular workpieces and complex contour surfaces.
|
CNC milling machine | Vertical milling machine: The spindle is vertical, supporting drilling, milling, and contour cutting, suitable for high-precision machining of small and medium-sized parts.
Horizontal milling machine: with a horizontal spindle, suitable for large material removal and mold manufacturing, with high efficiency but slightly lower accuracy.
|
Processing center | Integrating functions such as milling, drilling, and tapping, high-precision fixture structures can optimize the firmness of workpiece clamping; Some models are equipped with tool head twisting fixtures to improve the maintenance efficiency of milling cutters.
|
Drilling and planing machines | Used for hole machining and flat cutting, the CNC system can accurately control the machining parameters.
|
Grinding machine | By designing the grinding frame and milling cutter head to ensure the sharpness of the tool, it is commonly used for surface treatment of precision parts.
|
Special processing equipment | Water jet cutting machine: using high-pressure water jet to cut metal, glass and other materials, suitable for fine processing of complex patterns.
Router: Designed specifically for large parts, the tool moves vertically to improve machining efficiency.
The above equipment can be used separately or in combination according to processing requirements, and can be used in conjunction with fixtures, cutting tools, and CNC systems to achieve high-precision and high-efficiency automated production |
|
What CNC machining technologies and patents do we have
1、 Core technology composition |
Multi axis linkage technology | Five axis linkage technology allows machine tools to move simultaneously in multiple axes, enabling the machining of complex surfaces and irregular parts.
For example, through the design of sliding grooves and sliders, multiple loading platforms can be quickly switched to improve processing efficiency |
Automated fixtures and jigs | The CNC left and right machining fixture adopts a cylinder and thread linkage device to achieve rapid clamping and positioning of small workpieces. |
High speed machining (HSM) | By optimizing cutting speed and feed rate, shortening machining cycle, suitable for mass production scenarios, intelligent monitoring and optimization
Combining AI to adjust parameters in real-time, predict tool wear, and reduce downtime. |
2、 Technical advantagesHigh precision: The error is controlled at the micrometer level (± 0.01mm or even higher), meeting the high requirements of precision parts such as aerospace and medical equipment.
High efficiency and flexibility: Quickly switch processing tasks through program adjustments to meet small batch customization needs; Automated continuous processing reduces manual intervention and is suitable for mass production.
Consistency: The dimensions of mass-produced parts are highly consistent.
Efficiency improvement: Composite processing technology (such as turning milling composite) achieves multi process integration and reduces the number of clamping times.
Complexity: capable of achieving complex geometric shapes that are difficult to achieve manually or with traditional machine tools.
Additive subtractive composite processing: Combining 3D printing and CNC cutting to enhance the manufacturing capability of complex parts.
Green manufacturing: Laser assisted processing technology reduces energy consumption, improves material utilization, reduces waste, optimizes energy consumption, and uses environmentally friendly cutting fluids.
3、 Application FieldsPrecision manufacturing: such as mobile phone parts, automotive engine components.
Mold processing: Complex mold cavity processing relies on five axis linkage technology.
Emerging fields: Application of microfabrication technology in microsensors, optical components, etc.
Intelligent upgrade: Integrating AI to optimize machining parameters, real-time monitoring of tool wear, combined with industrial robots to achieve unmanned production lines, AI driven adaptive machining systems will further improve automation levels,
Modular design: Swap tooling to promote equipment functionality scalability.
|
CNC machining solution
|
 Here we introduce all the information about CNC machining, an AI based one-stop on-demand manufacturing service provider. We have over 50 self-developed CNC equipment engineers and over 80 prototype CNC machining design engineers; Having global CNC high-end precision equipment, CNC standard equipment, and self-developed modified CNC equipment; Thus achieving the requirements of simple accessories to complex and precise accessories (high-precision CNC small diameter cutting tools, with a minimum of 0.01 millimeters); And we have a CNC processed product surface treatment production line! You only need to upload 3D drawings or prototype accessories, and use materials. Our engineers will provide you with the required parts quotation and delivery time in half an hour. Our manufacturing network covers over 100000 manufacturers worldwide, supporting thousands of materials and hundreds of manufacturing processes, providing you with the production capacity you need to design and produce prototypes.
Here we introduce all the information about CNC machining, an AI based one-stop on-demand manufacturing service provider. We have over 50 self-developed CNC equipment engineers and over 80 prototype CNC machining design engineers; Having global CNC high-end precision equipment, CNC standard equipment, and self-developed modified CNC equipment; Thus achieving the requirements of simple accessories to complex and precise accessories (high-precision CNC small diameter cutting tools, with a minimum of 0.01 millimeters); And we have a CNC processed product surface treatment production line! You only need to upload 3D drawings or prototype accessories, and use materials. Our engineers will provide you with the required parts quotation and delivery time in half an hour. Our manufacturing network covers over 100000 manufacturers worldwide, supporting thousands of materials and hundreds of manufacturing processes, providing you with the production capacity you need to design and produce prototypes.





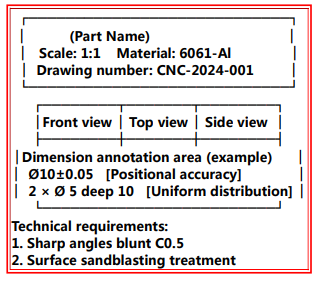

 +8613669807274
+8613669807274

